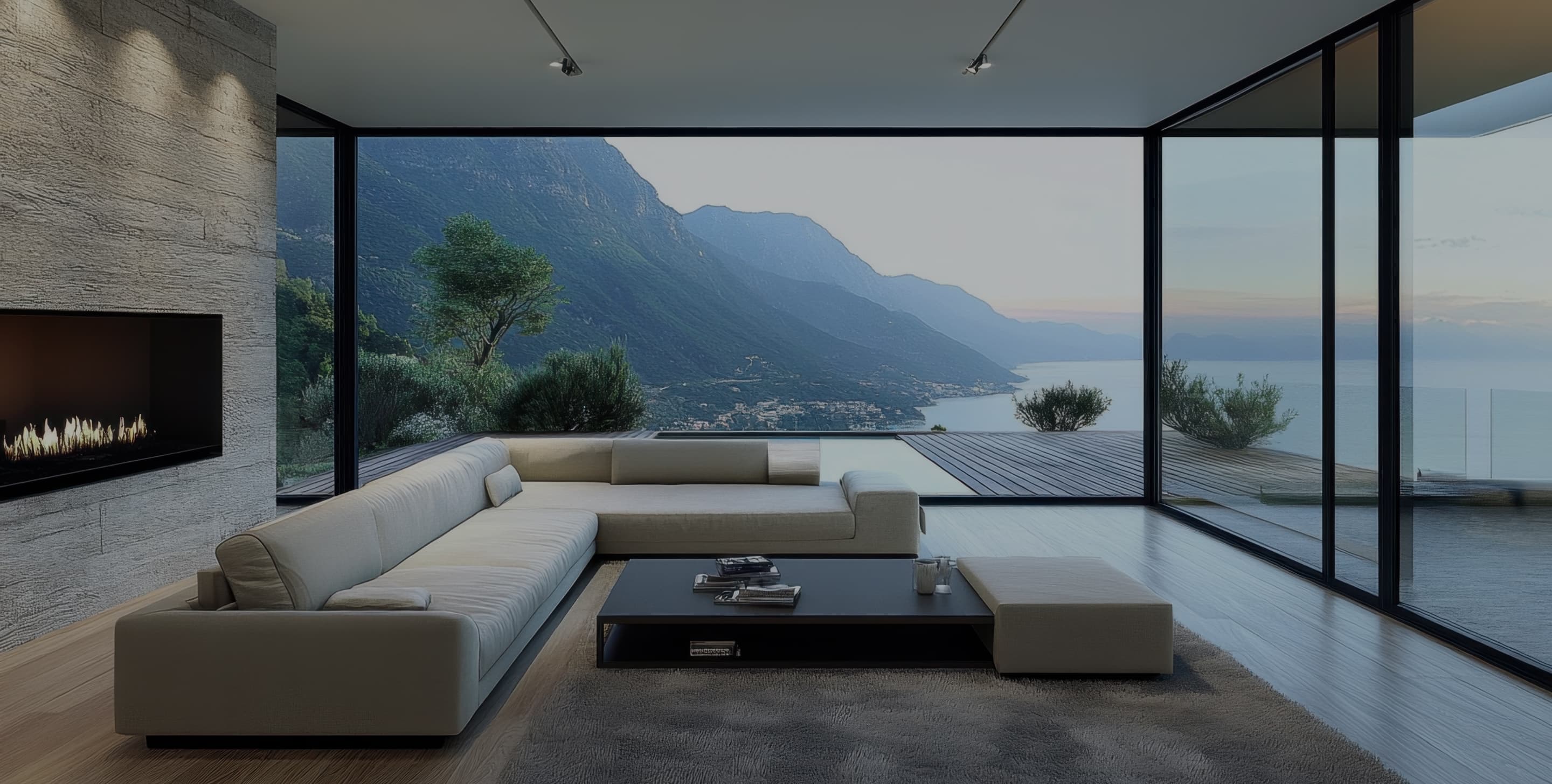

Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) is a technology that precisely
controls temperature, humidity, and air circulation to optimize the indoor environment.
The system integrates cooling, heating, and ventilation functions to play a key role in maintaining
the comfort and air quality of the indoor space. It provides coolness by lowering the indoor
temperature in summer and removing moisture, and keeps a warm and cozy space in winter.
In addition, it supplies fresh air, emits pollutants and odors from the room, and finely controls
humidity to create a healthy and stable environment.
In conclusion, the air conditioning system is an environmental solution that elaborately
designs indoor air quality and comfort beyond simple air conditioning devices and is an
essential element of modern living and space.

sources and
health impact
- • Carbon dioxide: affects learning ability and causes headaches and shortness of breath
- • Volatile organic compounds: Main cause of sick house syndrome! Long-term exposure can cause atopic dermatitis
- • Radon: WHO Class 1 Carcinogens Causing Lung Cancer
- • Ultrafine dust: Occurs not only from outside but also from indoor activities of dishes
Display Stage
| Displaying the screen |

125Hz
|

250Hz
|

500Hz
|

1kHz
|
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PM2.5 Ultrafine dust |
0~15 | 16~35 | 36~75 | 76~ |
| PM10 Fine dust |
0~30 | 31~80 | 81~150 | 151~ |
| CO2 Carbon dioxide |
400~ 600 |
601~ 1,000 |
1,001~ 2,000 |
2,001~ |
| TVOC Total volatile organic compounds |
0~300 | 301~ 600 |
601~ 2,000 |
2,001~ |
to maintain a pleasant environment
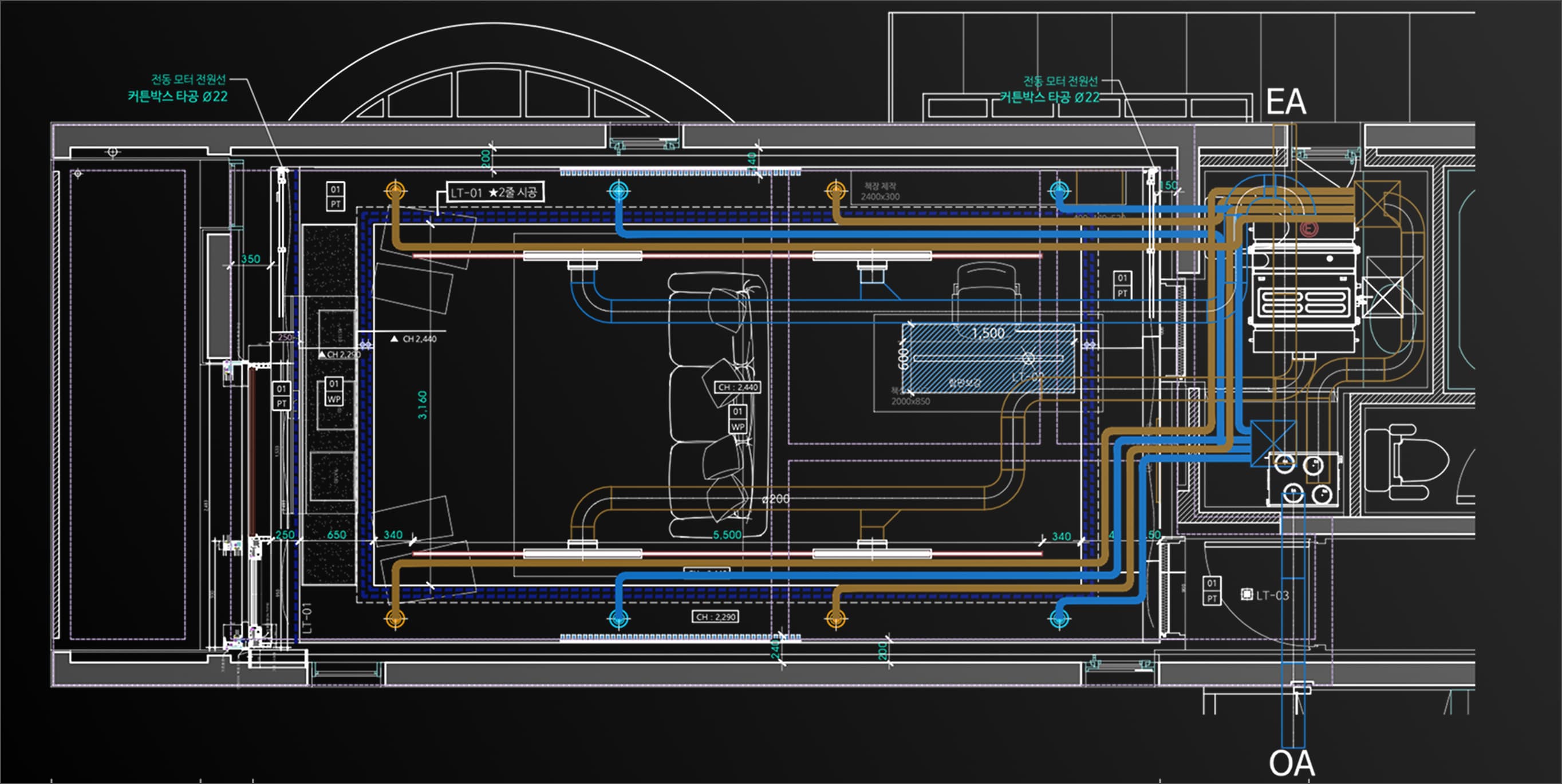
- • Supply air (Supply air, SA - fresh air supplied to the room via air conditioning system)
- • Ventilation air (Return air, RA - air used indoors is returned to the air conditioning system)
- • Outdoor air (Outdoor air, OA - fresh air from outside for indoor ventilation)
- • Exhaust Air (EA - Air that exudes polluted air from the room)


-
Virus Reduction
Decreased virus survival rate
Studies have shown that many viruses tend to be rapidly inactivated in the air when relative humidity is 40 to 60 percent. In particular, airborne viruses such as influenza have significantly lower survival rates in this range.
-
Mold Control
Inhibition of mold growth
When humidity exceeds 60%, mold
growth is promoted. Therefore, keeping
humidity at 40 to 60% can effectively
suppress mold problems in high
humidity environments. -
Protection
Respiratory Health Protection
Proper humidity protects the respiratory
mucosa, which reduces the risk of infection
and supports respiratory health.
Conversely, an overly dry environment
can stimulate the mucosa, increasing its
vulnerability to infection.
-
Air Conditioning
It provides a cool environment by lowering the indoor temperature in summer and removing excessive moisture. This maintains the comfort of the indoor space and healthy air quality.
-
Heating System
In winter, we create a cozy environment by controlling the indoor temperature warmly. It provides a stable and comfortable living environment even in cold weather.

